ideal perfect bite teeth alignment
Quick Answer: What Does a Perfect Bite Look Like?
A clinically ideal bite (Class I occlusion) typically occurs when:
- Upper teeth overlap lower teeth by approximately 2-4mm (about ⅔ coverage), varying by facial type
- Back teeth mesh like interlocking gears, with upper cusps resting in lower valleys
- Teeth contact harmoniously during function, without gaps or crowding
- Midlines align between upper and lower front teeth
- Arches form smooth U-shaped curves
- No pain when biting or chewing
This allows proper chewing, clear speech, and prevents jaw problems. According to orthodontic standards, slight variations from this ideal are common and often functionally acceptable.
What Perfect Teeth Alignment Looks Like: 3 Views
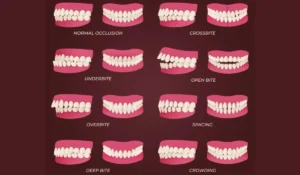
Quick Reference: Ideal Bite vs Common Problems
| View | Ideal Bite | Overbite | Underbite | Open Bite | Crossbite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front | Upper teeth overlap ⅔ of lower | Excessive overlap (>75%) | Lower teeth in front | Gap when closed | Some upper inside lower |
| Top | Smooth U-curve, no gaps | May appear normal | May appear normal | Spacing issues | Narrow upper arch |
| Side | Upper in front, mesh like gears | Too much overlap | Lower protrudes | Front/back don’t touch | Teeth crossed over |
1. Front View (Anterior View)
According to orthodontic evaluation standards used by the American Association of Orthodontists:
Ideal characteristics:
- Upper front teeth slightly overlap lower teeth
- Coverage: approximately ⅔ to ¾ of lower teeth visible (varies by facial type)
- Upper teeth edges roughly parallel to lower lip
- Midline (center line between front teeth) ideally aligns with nose and chin
- Balanced gum display when smiling
What to avoid:
- Deep bite: Upper teeth cover more than ¾ of lower teeth
- Open bite: Gap between upper and lower teeth when closed
- Overbite: Upper teeth stick out too far forward
- Underbite: Lower teeth sit in front of upper teeth
2. Top View (Occlusal View)
Looking down at teeth:
- Teeth form smooth U-shaped arch (like St. Louis Arch)
- Each tooth touches the next without gaps
- No overlapping or twisted teeth
- No crowding or spacing issues
- Upper arch slightly wider than lower arch
Both arches should:
- Show natural curve
- Have teeth touching at contact points
- Display no rotations or misalignment
3. Side View (Lateral View)
Ideal positioning:
- Upper teeth sit in front of lower teeth
- Back teeth mesh like interlocking gears
- Upper cusps (points) fit into lower valleys
- Upper front teeth backs rest gently against lower front teeth fronts
- No excessive overjet (upper teeth too far forward)
The “gear test”: Upper and lower molars should fit together perfectly, distributing chewing force evenly across all teeth.
Key Characteristics of Perfect Teeth
1. Proper Alignment
Straight positioning with no:
- Gaps between teeth
- Overlapping teeth
- Twisted or rotated teeth
- Crowding
- Excessive spacing
2. Correct Bite Relationship (Occlusion)
Class I occlusion (ideal):
- First upper molar fits perfectly with first lower molar
- Upper teeth slightly overlap lower teeth
- All teeth touch opposing teeth properly
3. Tooth Shape and Size
Proportional characteristics:
- Central incisors (front teeth): Rectangular with slightly rounded edges
- Lateral incisors: Slightly shorter than central incisors
- Canines: Pointed but not overly sharp, same length as central incisors
- Premolars and molars: Proper cusp height for chewing
Width-to-length ratio: Front teeth typically 75-80% as wide as they are long
4. Healthy Gums
Gum characteristics:
- Pink color (not red or pale)
- Firm texture
- No swelling or bleeding
- Proper gum line showing adequate tooth crown
- Not covering too much tooth (gummy smile)
- No recession exposing roots
5. Natural Color
Ideal tooth color:
- Natural white to light ivory shade
- Often harmonizes with facial features rather than pure white
- Consistent across all visible teeth
- No significant staining or discoloration
- Slight translucency at edges (healthy enamel characteristic)
Important: Excessively white teeth can appear artificial. Natural tooth enamel has subtle yellow or ivory undertones, which is completely normal and healthy.
6. Smooth Edges
Front teeth bottom edge:
- Smooth, not jagged or uneven
- Lateral incisors slightly shorter than central incisors
- Creates gentle, flowing curve
- No chips or fractures
Common Bite Problems (Malocclusion)
1. Overbite (Deep Bite)
Description: Upper teeth cover more than ¾ of lower teeth
Problems caused:
- Lower teeth bite into roof of mouth
- Excessive wear on front teeth
- Jaw pain
- Speech difficulties
Prevalence: Affects 15-20% of population
2. Underbite (Anterior Crossbite)
Description: Lower teeth sit in front of upper teeth
Problems caused:
- Difficulty chewing
- Jaw strain
- Facial asymmetry
- Speech issues
Prevalence: Affects 5-10% of population
3. Crossbite
Description: Some upper teeth sit inside lower teeth
Types:
- Posterior crossbite: Back teeth affected
- Anterior crossbite: Front teeth affected
Problems caused:
- Uneven tooth wear
- Jaw shifting to one side
- Facial asymmetry
- Gum recession
4. Open Bite
Description: Gap between upper and lower teeth when mouth closed
Types:
- Anterior open bite: Gap at front teeth
- Posterior open bite: Gap at back teeth
Causes:
- Thumb sucking
- Tongue thrusting
- Genetics
- TMJ disorders
5. Crowding
Description: Not enough space for all teeth
Problems caused:
- Difficult to clean
- Increased cavity risk
- Gum disease
- Uneven wear
6. Spacing (Diastema)
Description: Gaps between teeth
Problems caused:
- Food trapping
- Gum problems
- Aesthetic concerns
- Speech issues
Why Perfect Teeth Alignment Matters
1. Better Oral Health
Straight teeth are easier to clean:
- Effective brushing reaches all surfaces
- Flossing works properly
- Less plaque buildup
- Lower cavity risk
- Reduced gum disease
Clinical studies suggest properly aligned teeth may significantly reduce the risk of periodontal disease due to improved access for cleaning.
2. Proper Chewing Function
Ideal bite improves digestion:
- Even force distribution across teeth
- Efficient food breakdown
- Reduced strain on jaw muscles
- Better nutrient absorption
3. Clear Speech
Proper alignment aids pronunciation:
- Correct tongue placement
- Better airflow
- Clear consonant sounds (S, T, D, L)
- Reduced speech impediments
4. Prevents Jaw Problems
Reduces TMJ (temporomandibular joint) issues:
- Less jaw pain
- Fewer headaches
- Reduced muscle tension
- Prevented joint damage
5. Even Tooth Wear
Protects tooth structure:
- Prevents premature enamel erosion
- Reduces cracking and chipping
- Extends tooth lifespan
- Avoids costly repairs
6. Better Breathing
Proper jaw alignment supports airways:
- Reduced snoring
- Lower sleep apnea risk
- Better oxygen intake
- Improved sleep quality
How to Check Your Own Bite
Self-Assessment Steps
1. Front view check:
- Smile naturally in mirror
- Check if upper teeth cover ⅔ of lower teeth
- Verify midline alignment with nose
- Look for gum balance
2. Top view check:
- Open wide and look down
- Use phone camera to photograph
- Check for gaps or crowding
- Verify U-shaped arch
3. Side view check:
- Take side profile photo
- Check upper teeth position relative to lower
- Look for overbite or underbite
- Verify jaw alignment
4. Bite test:
- Bite down gently
- Notice where teeth contact
- Check for comfort (no pain)
- Listen for clicking or popping
When to see an orthodontist:
- Pain when biting
- Visible misalignment
- Difficulty chewing
- Jaw clicking or popping
- Excessive tooth wear
- Speech problems
Causes of Misaligned Teeth
Genetic Factors
Inherited traits:
- Jaw size and shape
- Tooth size
- Skeletal structure
- Family bite patterns
Research suggests the majority of malocclusions have a significant genetic component, though environmental factors also play important roles.
Childhood Habits
Detrimental behaviors:
- Prolonged thumb sucking (after age 4)
- Pacifier use (beyond age 3)
- Tongue thrusting
- Mouth breathing
- Nail biting
Dental Issues
Problems that affect alignment:
- Early tooth loss
- Extra teeth (supernumerary)
- Missing teeth (hypodontia)
- Large tooth-jaw size discrepancy
Injury or Trauma
Causes of damage:
- Facial injury
- Jaw fracture
- Tooth damage from accident
- Sports injuries
Other Factors
Additional influences:
- Gum disease causing tooth shifting
- Tooth grinding (bruxism)
- Poor dental work
- Tumor or cyst in jaw
How to Achieve Perfect Teeth Alignment
1. Traditional Metal Braces
How they work:
- Metal brackets bonded to teeth
- Wire connects brackets
- Gradual pressure moves teeth
- Rubber bands adjust bite
Best for:
- Severe misalignment
- Complex bite issues
- All ages
- Most affordable option
Treatment time: 18-36 months average
Cost: $3,000-$7,000
2. Clear Ceramic Braces
Advantages:
- Tooth-colored brackets
- Less visible than metal
- Same effectiveness
- Adult-friendly
Treatment time: 18-36 months
Cost: $4,000-$8,000
3. Clear Aligners (Invisalign)
How they work:
- Custom transparent trays
- Changed every 1-2 weeks
- Removable for eating/brushing
- Digital treatment planning
Best for:
- Mild to moderate issues
- Adults and teens
- Those wanting discreet treatment
- Disciplined wearers (22 hours/day)
Treatment time: 6-24 months
Cost: $3,500-$8,000
4. Lingual Braces
Features:
- Brackets on back of teeth
- Completely invisible from front
- Custom-made
- Effective for complex cases
Treatment time: 18-36 months
Cost: $8,000-$13,000
5. Palatal Expanders
Purpose:
- Widen narrow upper jaw
- Create space for teeth
- Prevent crossbite
- Used in growing children
Treatment time: 3-6 months active expansion
Cost: $2,000-$3,000
6. Retainers
After treatment:
- Maintain teeth position
- Prevent shifting
- Worn full-time initially
- Eventually only at night
Types:
- Removable clear retainers
- Fixed permanent retainers
- Hawley retainers
Cost: $200-$600
Treatment Timeline
Phase 1: Early Intervention (Ages 7-10)
Goals:
- Guide jaw growth
- Create space for permanent teeth
- Address thumb sucking
- Correct crossbite
Duration: 6-12 months
Phase 2: Comprehensive Treatment (Ages 11-14)
Goals:
- Align all permanent teeth
- Correct bite problems
- Achieve ideal occlusion
- Finish smile aesthetics
Duration: 18-24 months
Adult Treatment (Age 18+)
Considerations:
- Bone density lower
- Treatment may take longer
- More aesthetic options available
- Higher cost in some cases
Duration: 12-36 months
Maintaining Perfect Teeth Alignment
Daily Habits
Essential practices:
- Brush twice daily (2 minutes each)
- Floss once daily
- Use fluoride toothpaste
- Rinse with mouthwash
- Avoid hard/sticky foods
Professional Care
Regular checkups:
- Dental cleanings: Every 6 months
- Orthodontic checkups: Every 6-8 weeks during treatment
- X-rays: Annually or as needed
Retainer Wear
Critical for success:
- Wear as directed (usually full-time for 3-6 months)
- Transition to night-only wear
- Maintain lifelong (teeth naturally shift with age)
- Clean daily with gentle soap
Clinical note: Research indicates that relapse is common when retainers aren’t worn as prescribed, with significant tooth movement possible within the first year. Individual relapse risk varies based on original malocclusion severity and biological factors.
Lifestyle Choices
Protect your investment:
- Wear mouthguard for sports
- Don’t use teeth as tools
- Limit staining foods/drinks
- Quit smoking
- Manage teeth grinding with night guard
Perfect Teeth vs. Natural Variation
Important Reality Check
Perfect teeth are rare:
- Studies estimate only a small percentage (approximately 5-10%) naturally have ideal occlusion in all respects
- Slight variations are normal and common
- Function matters more than textbook perfection
- Natural teeth have individual character
When Treatment Is Needed
Medical indications:
- Pain when eating
- TMJ problems
- Excessive tooth wear
- Breathing difficulties
- Speech impediments
- Jaw strain
Cosmetic considerations:
- Personal confidence
- Professional appearance
- Social comfort
- Smile satisfaction
When to Accept Natural Teeth
If you have:
- No pain or functional issues
- Easy oral hygiene maintenance
- No excessive wear
- Comfortable bite
- Acceptable aesthetics
Remember: Healthy teeth don’t have to be “perfect” to be beautiful and functional.
Frequently Asked Questions
How far should my upper teeth overlap my lower teeth?
Answer: In a clinically ideal bite, upper teeth typically overlap lower teeth by approximately 2-4mm, covering about two-thirds of the lower front teeth. The exact amount varies based on individual facial structure, skeletal pattern, and incisor inclination. More than 4-5mm is generally considered a deep bite; less than 1mm or no overlap indicates an open bite. Your orthodontist evaluates this in context with your overall facial structure.
Should my teeth touch when my mouth is closed?
Answer: Your teeth should contact harmoniously during function (chewing, swallowing) but typically don’t touch at complete rest. When you bite down gently, back teeth (molars) should mesh together, and front teeth should have light contact. At rest, there’s usually a small space (freeway space) between upper and lower teeth. Constant clenching or grinding indicates a problem. If your teeth don’t contact properly during chewing, you may have an open bite or alignment issue.
What does Class 1 bite mean?
Answer: Class I bite is the ideal bite relationship where the first upper molar fits perfectly into the groove of the first lower molar, like a key in a lock. This is considered the “perfect bite” and allows for optimal chewing function and even tooth wear.
Can adults get perfect teeth alignment?
Answer: Yes, adults can achieve excellent teeth alignment with orthodontic treatment. However, treatment may take longer than in children because bone density is higher. Options include braces, Invisalign, or in severe cases, combined orthodontics and jaw surgery.
How do I know if my bite is off?
Answer: Signs of misaligned bite include: jaw pain or clicking, difficulty chewing, uneven tooth wear, frequent headaches, teeth grinding, speech difficulties, or visible misalignment. A dentist or orthodontist can diagnose bite problems through examination and x-rays.
Is a perfect bite achievable for everyone?
Answer: Most people can achieve a functional, healthy bite that’s very close to ideal with orthodontic treatment. True “perfection” (ideal in every measure) is rare, but significant improvement is possible for 95% of patients. Goals focus on function and health, not just aesthetics.
Do straight teeth mean a perfect bite?
Answer: No. Straight front teeth don’t guarantee a perfect bite. Your back teeth must also align properly, your jaw position must be correct, and your bite must function well. You can have straight-looking teeth but still have bite problems affecting your jaw and overall function.
Summary
Clinically ideal teeth alignment involves proper bite relationship (occlusion), straight positioning, healthy gums, and functional harmony. An ideal bite typically features upper teeth overlapping lower teeth by approximately 2-4mm, back teeth meshing like interlocking gears, minimal gaps or crowding, and aligned midlines. While textbook perfection is rare (studies suggest only 5-10% naturally achieve this), orthodontic treatments like braces or clear aligners can significantly improve alignment for better oral health, function, and aesthetics. The goal of treatment is functional excellence and individual facial harmony rather than absolute uniformity. Treatment success requires professional evaluation, appropriate technique selection based on your specific needs, and long-term retainer use. Remember: healthy, functional teeth matter more than achieving every textbook measurement—slight natural variations are often perfectly acceptable.
When to Seek Professional Evaluation
If you’re experiencing any of the following, an orthodontic consultation can help determine whether treatment would benefit you:
- Pain or discomfort when chewing
- Jaw clicking, popping, or locking
- Difficulty cleaning between teeth
- Visible misalignment affecting confidence
- Speech difficulties
- Uneven tooth wear
- Frequent headaches or jaw tension
Professional assessment is the only way to accurately diagnose bite problems. Many issues that seem minor can have functional implications, while some visible imperfections may not require treatment. An orthodontist can evaluate your bite in three dimensions, review x-rays, and discuss whether intervention would improve function, health, or aesthetics.
Ready to restore your smile? Contact EliteFixDenture in Chicago today:
Visit Us: Elite Fix Denture, 737 N Michigan Ave, Chicago, IL 60611
Call Today: +1 312-263-7823
Reviewed by: Dr. Aziz Liaquat, Lead Dentist
Medical Disclaimer: This article provides educational information only. Consult a licensed dentist or orthodontist for personalized diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Every mouth is unique and requires professional evaluation.