Candizi
“Candizi” appears to be a misspelling or variant shorthand for candidiasis (also called Candida infection or yeast infection), a common fungal overgrowth caused by Candida yeasts like C. albicans. This condition affects millions yearly, disrupting skin, mucosal, or systemic balance in the body. Proper recognition and care enhance overall health resilience.
What Is Candidiasis?
Candidiasis is a common fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida, a type of yeast that naturally lives in small amounts on your skin, mouth, intestines, and other areas of the body. While Candida is normally harmless when kept in balance by healthy bacteria, certain conditions can cause it to multiply rapidly and lead to infection.
This yeast infection occurs when the balance between healthy bacteria and Candida yeast in your body becomes disrupted. The most common culprit is Candida albicans, though other species can also cause infections.
Common Types of Candidiasis
Candidiasis can affect various parts of the body:
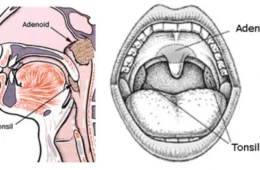
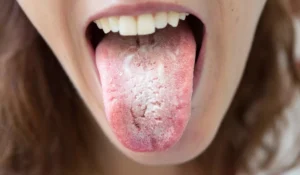
Oral Candidiasis (Thrush): Appears as white patches in the mouth and throat, commonly affecting infants, toddlers, and people with weakened immune systems.
Vaginal Yeast Infections: One of the most common forms, affecting the vagina and vulva with symptoms like itching, discharge, and discomfort.
Skin Candidiasis: Develops in warm, moist areas of the body such as skin folds, armpits, and under the breasts.
Invasive Candidiasis: A serious form where the yeast enters the bloodstream and spreads to internal organs, primarily affecting hospitalized patients or those with compromised immune systems.
Recognizing the Symptoms
General Symptoms
Common symptoms include mouth lesions, persistent fatigue, and various digestive issues. Many people experience:
- Chronic tiredness and low energy
- Brain fog and difficulty concentrating
- Digestive problems including bloating, gas, and changes in bowel movements
- Skin issues like rashes, eczema, or fungal nail infections
- Intense sugar cravings
Vaginal Yeast Infection Symptoms
Vaginal infections typically cause intense itching in the vagina and around the vulva, accompanied by redness, soreness, and a thick white discharge.
Oral Thrush Symptoms
White or cream-colored patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, roof of the mouth, or throat. These patches may bleed slightly when scraped.
Serious Warning Signs
Medical care should be sought if symptoms are severe, persist beyond a few days, or recur frequently, particularly for people with diabetes or weakened immune systems.
What Causes Candida Overgrowth?
Understanding the triggers can help you prevent future infections:
Primary Risk Factors
Antibiotic Use: Antibiotics can kill beneficial bacteria that normally keep Candida under control, allowing yeast to proliferate.
Compromised Immune System: People with HIV, cancer, or those taking immunosuppressive medications are at higher risk.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes with persistently high blood sugar levels promotes yeast growth.
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menstrual cycles, and birth control pills can alter the body’s hormonal balance, creating conditions favorable for yeast overgrowth.
Diet High in Sugar and Refined Carbs: Yeast thrives on sugar, so diets heavy in sweets and processed foods can fuel overgrowth.
Prolonged Moisture: Wearing tight clothing or staying in wet swimwear creates warm, moist environments where Candida flourishes.
Diagnosis and Testing
Healthcare providers typically diagnose candidiasis through:
- Physical Examination: Visual inspection of affected areas
- Medical History Review: Discussion of symptoms and risk factors
- Laboratory Testing: Cultures from affected areas, blood tests, or stool analysis for more comprehensive evaluation
Comprehensive stool testing can detect Candidiasis in the colon or lower intestines, with labs able to identify the specific yeast species and determine effective treatments.
Treatment Options
Mild to Moderate Infections
Antifungal medications can effectively treat and clear infections within two days to two weeks. Treatment varies based on infection location:
For Vaginal Infections:
- Over-the-counter antifungal creams (1, 3, or 7-day treatments)
- Single-dose oral fluconazole prescription
For Oral Thrush:
- Antifungal lozenges or mouthwashes
- Oral antifungal medications
For Skin Infections:
- Topical antifungal creams or powders
- Keeping affected areas clean and dry
Severe or Invasive Infections
The recommended antifungal treatment for invasive candidiasis in most adults includes echinocandins administered intravenously, though fluconazole and amphotericin B may also be appropriate depending on the situation.
Natural Support Approaches
While medical treatment is primary, certain dietary and lifestyle changes may support recovery:
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables help restore healthy gut bacteria
- Antifungal Foods: Garlic, coconut oil, oregano oil, and ginger have natural antifungal properties
- Reduced Sugar Intake: Limiting sugar and refined carbohydrates starves yeast cells
- Adequate Hydration: Drinking plenty of water supports overall health and detoxification
Prevention Strategies
Daily Practices
- Practice Good Hygiene: Keep skin clean and dry, especially in fold areas
- Wear Breathable Clothing: Choose cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting garments
- Manage Blood Sugar: Keep diabetes well-controlled through diet, exercise, and medication
- Use Antibiotics Wisely: Only take antibiotics when medically necessary
- Maintain Oral Health: Brush teeth twice daily and floss regularly
Dietary Considerations
Research suggests that reducing dietary sugar may help prevent yeast infections, as foods high in sugar, refined grains, and processed products can promote Candida growth.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Symptoms that don’t improve with over-the-counter treatments
- Recurring infections (four or more per year)
- Severe symptoms affecting daily life
- Signs of systemic infection like fever, chills, or widespread rash
- Any symptoms if you’re immunocompromised
Recovery Timeline
For mild cases caught early with consistent dietary and lifestyle changes, improvements may appear within a few weeks, while moderate to severe cases may require several months to fully restore balance.
The healing process involves not just eliminating excess yeast but also repairing the gut lining and rebuilding healthy bacterial populations.
Living with Recurrent Candidiasis
Some people experience chronic or recurrent infections. Working with a healthcare provider to identify underlying causes is crucial. This might involve:
- Comprehensive immune system evaluation
- Hormonal testing
- Dietary assessment and modifications
- Long-term antifungal protocols
- Probiotic supplementation
The Bottom Line
Candidiasis is a manageable condition when properly diagnosed and treated. While mild infections often respond well to over-the-counter treatments, persistent or severe cases require professional medical care. By understanding your risk factors and taking preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing this common fungal infection.
Remember that maintaining balance in your body’s natural microbiome through healthy diet, stress management, and appropriate use of medications is key to keeping Candida in check. If you suspect you have candidiasis, consult with a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.